It is used as rectifiers and used in alternating current. Sources Found in certain zinc ores.
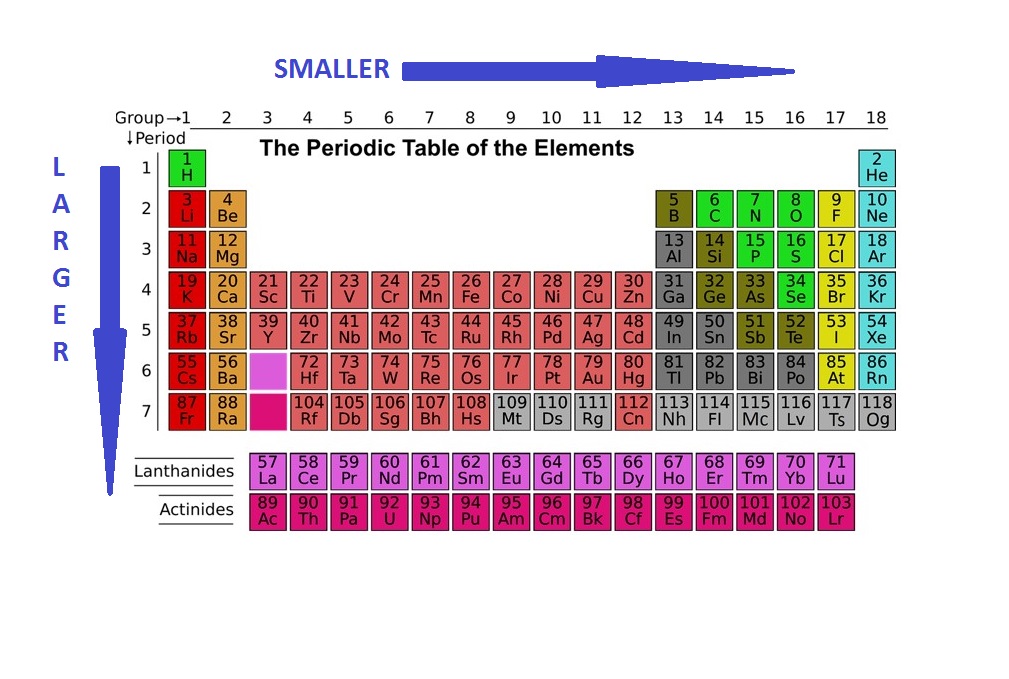 Understanding Atomic Radius Trends The 2 Key Principles
Understanding Atomic Radius Trends The 2 Key Principles
Watch this video to learn everything you ever wanted to know about Indium.

Atomic radius of indium. The atomic radius of a chemical element is a measure of the distance out to which the electron cloud extends from the nucleus. The atomic radius of Indium atom is 142pm covalent radius. Ionic radius r ion is the radius of a monatomic ion in an ionic crystal structure.
Atomic radius of Tin Sn 217 pm. 157 cm³mol Density 293 K. All measurements given are in picometers pm.
080 Å 3 Covalent radius. It must be noted atoms lack a well-defined outer boundary. However it is chemically more similar to gallium and thallium.
200 Å Ionic radius. 193 pm Van der Waals Atomic Symbol. Indium Facts Indium Covalent Radius 144 Å Atomic Number 49 Learn more about the atomic number.
It is also use to make mirrors. Atomic radius of Xenon Xe 216 pm. 7 Zeilen The atomic radius of Indium atom is 142pm covalent radius.
Atomic radius of Barium Ba 268 pm. Relativly small amounts are used in dental items and in electronic semiconductors. The atomic radius of a chemical element is a measure of the distance out to which the electron cloud extends from the nucleus.
Indium is use as photoconductor. 1274 GPa in tension. 731 gcm³ Crystal structure.
4 Zeilen Atomic Number. It is a silvery-white metal that most closely resembles tin in appearance. Indium is use in semiconductor device which is use in transistors.
Orbital Radius pm Radius AU Periodicity link. Atomic radius of Caesium Cs 343 pm. K MPa 295 16 76 150 4 319 Compressive strength.
119 Zeilen Atomic radius. State at 20 C Solid Uses Used to coat high speed bearings and as an alloy that lowers the melting point of other metals. Kr4d105s25p1 First ionization energy.
Atomic radius of indium is 156 Pm. Except for the alkali metals indium is the softest metal. Atomic radius of Indium In 193 pm.
Atomic radius of Iodine I 198 pm. Valence shell orbital radii for indium. The atomic radius of Indium atom is 142pm covalent radius.
Sources Found in certain zinc ores. Atomic Mass 114818 Learn more about the atomic mass. Part 2 of 2.
Relativly small amounts are used in dental items and in electronic semiconductors. Calculation of the density of Indium from its atomic radius and face-centered cubic fcc lattice structure. 144 Å Atomic volume.
It must be noted atoms lack a. Description Rare very soft silver-white metal Atomic. It must be noted atoms lack a well-defined outer boundary.
133k-calg-mole Mechanical Properties Tensile strength. 49 Photoelectric work function. Indium is a chemical element with atomic number 49 and element symbol In.
Valency valency of indium is 3. Atomic radius of Antimony Sb 206 pm. Although neither atoms nor ions have sharp boundaries they are sometimes treated as if they were hard spheres with radii such that the sum of ionic radii of the cation and anion gives the distance between the ions in a crystal latticeIonic radii are typically given in units of either picometers pm or.
Its alloy form use in Fire sprinkler it have low melting point hence it is use in fire sprinklers. Atomic radius of Tellurium Te 206 pm. Indium Data Indium Atomic Radius 200 Å State at 20 C Solid Uses Used to coat high speed bearings and as an alloy that lowers the melting point of other metals.
09HB Elastic modulus at 20C.
Orbital Radius pm Radius AU Periodicity link. Check all that applytravel in straight lines and can bounce off surfacestrav.
 Does Lithium Ion Have Bigger Radius Than Bromine Ion Or Not Quora
Does Lithium Ion Have Bigger Radius Than Bromine Ion Or Not Quora
Valence shell orbital radii for bromine.
Atomic radius of bromine. Speaking of Bromine let me walk you through some interesting details. 3 Li - Lithium. There are cool facts about Bromine that most dont know about.
Learn more about the atomic radius here. It must be noted atoms lack a. Atomic radius of lithium is 134 pm.
119 Zeilen Atomic radius. It must be noted atoms lack a well-defined outer boundary. 7 Zeilen The atomic radius of Bromine atom is 120pm covalent radius.
El through space at the speed of. Fluorine chlorine bromine and iodine. 119 Zeilen Atomic radius of Promethium Pm 236 pm.
In the first layer it has 2 electrons in the second it has 8 electrons in its third layer it has 18 electrons and in the fourth one 7 electrons. Bromine has a total of 35 electrons whose distribution is as follows. Atomic radii decrease however as one moves from left to right across the Periodic Table.
Image showing periodicity of valence s-orbital radius. This page discusses the trends in the atomic and physical properties of the Group 7 elements the halogens. Element Atomic Number Element Symbol Element Name Element Element Atomic Radius 1.
In the case of Bromine the atomic radius is 112 Å. Atomic Radius of Bromine The atomic radius of Bromine atom is 120pm covalent radius. Although more electrons are being added to atoms they are at.
In the case of Bromine the ionic radius is 196 -1 Å. The general trend is that atomic sizes increase as one moves downwards in the Periodic Table of the Elements as electrons fill outer electron shells. 1 H - Hydrogen.
The chemical symbol for Caesium is Cs. New questions in Chemistry PLEASE ANSWER QUICK which are characteristics of electromagnetic waves. Atomic radii represent the sizes of isolated electrically-neutral atoms unaffected by bonding topologies.
Sections below cover the trends in atomic radius electronegativity electron affinity melting and boiling points and solubility including a discussion of the bond enthalpies of halogen-halogen and hydrogen-halogen bonds. Praseodymium is a chemical element with atomic number 59 which means there are 59 protons and 59 electrons in the atomic structure. All measurements given are in picometers pm.
Atomic radius of bromine 2 See answers nicoleperez870 nicoleperez870 Answer. The answer is 185 Pm. Lithium atoms are bigger than bromine atoms.
183 pm Van der Waals Atomic Symbol. Atomic radius of bromine is 114 pm. The atomic radius of a chemical element is a measure of the distance out to which the electron cloud extends from the nucleus.
The chemical symbol for Nobelium is No. 2 He - Helium. Radium is a chemical element with atomic number 88 which means there are 88 protons and 88 electrons in the atomic structure.
The average radius for bromine is 115 pm its atomic radius or Bohr radius is 94 pm its covalent radius is 114 pm and its Van der Waals radius is 185 pm.
Atomic number and mass number are always whole numbers because they are obtained by counting whole objects protons neutrons and electrons. The average mass of a chemical element expressed in atomic mass units.
Why Is The Word Average Used In The Definition Of Atomic Mass Quora
According to the definitions given atomic mass which is also called atomic weight is the measured total mass of an elements atom.

Define atomic number and atomic weight. The atomic weight of an element having more than one principal isotope is calculated both from the atomic masses of the isotopes and from the relative abundance of each isotope in nature. The Atomic weight is defined as the. Atomic Number and Atomic Weight The atomic weight or the relative atomic mass is the ratio of the average atomic mass of an atom to some reference standard.
When molecular mass expressed in gram is called gram molecular weight. The mass number reports the mass of the atoms. In learning chemistry the molecular mass or weight of the compound meaning the number that indicates how heavy a molecule of the compound is compared to one-twelfth of the carbon-12 isotope atomic number 12.
Atoms of different elements usually have different mass numbers. Atomic number has no units. Number of electrons in a neutral atom Mass Number.
The mass number is a count of the total number of protons and neutrons in an atoms nucleus. Number of protons and neutrons combined in its nucleus. The mass number of an atom is its total number of protons and neutrons.
The atomic number of an atom is the number of protons in its nucleus ie. Whereas atomic number is nothing but the total number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of an atom. An experimentally determined number characteristic of a chemical element that represents the number of protons in the nucleus which in a neutral atom equals the number of electrons outside the nucleus and that determines the place of the element in the periodic table see Chemical Elements Table.
It is the weighted average of the masses of naturally-occurring isotopes. Atomic mass is also known as atomic weight. The mass number of an atom is the total number of nucleons ie.
What Is It Based On. Other atoms dont generally have round-number atomic masses for reasons that are a little beyond the scope of this article. 120 Zeilen Definition of Atomic Weight.
Atomic number and mass number - definition. Atomic number is the total number of protons present in the nucleus of an atom. Atomic mass is the weighted average mass of an atom of an element based on the relative natural abundance of that elements isotopes.
Prior to 1961 a unit of atomic weight was based on 116th 00625 of the weight of an oxygen atom. By definition an atom of carbon with six neutrons carbon-12 has an atomic mass of 12 amu. Atomic weight is the average mass of atoms of an element calculated using the relative abundance of isotopes in a naturally-occurring element.
The atomic mass of a single atom is simply its total mass and is typically expressed in atomic mass units or amu. A normal helium atom for example has two protons and two neutrons in its nucleus with two electrons in orbit. Difference Between Atomic Mass and Atomic Number.
Under what conditions are two atoms different isotopes of the same element. The dimensionless standard atomic weight is the weighted mean relative isotopic mass of a typical naturally-occurring mixture of isotopes. The atomic mass of atoms ions or atomic nuclei is slightly less than the sum of the masses of their constituent protons neutrons and electrons due to binding energy mass loss per E mc2.
If the reference standard is considered 1 u the atomic weight is the ratio of the average atomic mass to one unified mass unit 1 u. The sum of the mass number and the atomic number for an atom A-Z corresponds to the total number of subatomic particles present in the atom. Define atomic number and atomic mass number.
Each atom therefore can be assigned both an atomic number the number of protons equals the number of electrons and an atomic weight approximately equaling the number of protons plus the number of neutrons. Mass of protons AND of neutrons in an atomAtomic of protons in an atomIsotopes of an element Atoms of an element with the same atomic numbe. Difference Between Atomic Number and Atomic Weight Definition.
Atomic weight is given in amu atomic mass units. Definition of atomic number.